In this issue, we provide:
- An update on the US Department of Energy CALiPER solid state lighting testing program.
- Feedback on from the IEC TC34 panel meetings in Milan.
- An update on progress with the lites.asia collaborative projects.
- Details of the next lites.asia meeting.
- Information on the proposed framework for an IEC Electrical Energy Efficiency Labeling Program.
We also continue the series of special features on national standards and labelling programmes from around the region with a feature on the Philippines.
US DOE Releases CALiPER Application Summary Report on LED PAR38 Lamps
The US Department of Energy CALiPER program supports the testing of a wide array of solid-state lighting products (otherwise known as LED lighting) available in the USA. The testing programme seeks to capture the current state of the market – a cross section ranging from expected low- to high-performing products – with the bulk of those tested characterising the average of the range.
The most recent report, Report 20, evaluates the independently tested photometric performance of 38 LED PAR38 (reflector) lamps.
The results show significant improvement against earlier CALiPER testing of similar products. All of the LED PAR38 lamps tested offer substantial energy savings compared to halogen PAR38 lamps, and some are more efficient than compact fluorescent or ceramic metal halide versions. In addition to efficacy, the study also investigated parameters such as colour quality, beam angle and power factor.
A summary of the results is now available to download on the US Department of Energy solid-state lighting website.
Feedback from IEC TC34 panel meetings in Milan
The International Electrotechnical Commission TC34 (Lighting Committee) panel meetings and workshops were held recently in Milan, Italy from 14 to 25 January. Attendance from the Asia-Pacific region included attendees from the Philippines, Vietnam, Australia, Indonesia, China, Japan, and the Republic of Korea. The meetings focused on technical drafting and review of a range of IEC performance and safety standards for lighting. Much of the time was devoted to continued development of standards and terms and definitions for LED lighting, however there was also work on standards for compact fluorescent lamps.
Of interest to lites.asia stakeholders was the further work on IEC 60969 CFLi Performance Standard, where it was pleasing to see significant progress towards producing a final revised standard. Time was also allocated to discussion of the proposed Technical Specification for CFL Performance Tiers. This proposal has received a mixed response from TC34 participants. Attendees from a number of countries attending the workshop, including lites.asia countries, spoke in support of the proposal. However attendees from some other countries expressed reservations about the proposal. The proposal has also been circulated as a draft for comment by National Committees and collated comments are available from National Standards committees – (CC)34A-1639-DC-REV1. Further discussion is expected at the next TC34 PRESCO meeting in Korea on 8 April 2013. The lites.asia resolution in support of the Technical Specification (an outcome of the Delhi lites.asia meeting) was circulated in advance and was discussed at the meeting.
Another interesting issue that arose during the meetings was the topic of sample size for IEC lighting performance standards. It was noted that most of the performance standards state that they are intended for type testing, which may often only require one sample. However it was acknowledged that sample sizes in these standards also serve as guidance for production testing and compliance. One option might be to make use of informative annexes to provide guidance of sample sizes across a range of applications. A paper is to be prepared for further discussion at the next PRESCO meeting in Korea.
Update on progress with lites.asia collaborative projects
At the Hanoi lites.asia meeting in June 2012, it was agreed that lites.asia members would seek to collaborate on four projects:
- National labelling compliance surveys.
- Training for testing laboratory staff.
- ‘Meeting the Suppliers’ events.
- Creation of a ‘Communications Materials Library’.
Three of these projects are now well underway:
National labelling compliance survey
The methodology and support material have been compiled for the project and firm commitment has been received from Australia, Pakistan, the Philippines, Sri Lanka, Thailand and Vietnam to participate in the project. It is hoped that Indonesia and India will be able to join the project later in the year. The aim of the project is to:
- Improve national understanding of levels of labelling compliance.
- Identify the key areas of similarity, or variation, in labelling non-compliance in the region, including by type of retail outlet, product category or brand.
- Measure the improvement in compliance rates through increased market surveillance and communication with suppliers.
A full description of the project is available on the lites.asia website.
‘Meeting the Suppliers’ events
Following on from the successful pilot event – Informing the Suppliers – held in conjunction with the Delhi lites.asia meeting in October 2012 and attended by 30 industry representatives, discussions are underway to host a second meeting following the next lites.asia meeting in Indonesia in April 2013. Please contact us at if you are interested in attending this event.
Creation of a ‘Communications Materials Library’
Following agreement of the specification for the lites.asia communications material library at the lites.asia meeting in Delhi in October 2013, a beta-version of the library has been developed and populated with sample material submitted by Australia. The library is currently being reviewed by a team of core lites.asia members and it is expected that it will be publically available on the lites.asia website in March 2013. If you have any material (either documents or website links) that you would like to contribute to the library, please email it to us at .
Seventh lites.asia meeting to be held in Indonesia
The next lites.asia meeting will be held in Jakarta, Indonesia on 22-23 April 2013. While feedback is still being sought on the full agenda, the meeting will include updates on IEC activities of interest to members, discussions on progress of the regional labelling compliance survey, a special session on how the region is addressing the savings opportunities available from use of day lighting, and an introduction to the expanding activities of the UNEP’s en.lighten programme across the region.
IEC considering introduction of an IEC Electrical Energy Efficiency Labelling Program
Energy labelling programs form a key part of many national energy efficiency policies, aiming to encourage the preferential uptake of energy efficient products. It is the view of the IEC Conformity Assessment Board (CAB) that harmonization of electrical energy efficiency labels would facilitate global trade of these products and assist energy efficiency policy implementation.
This view is built on the vast practical experience and accumulated success that the IEC Conformity Assessment Systems have demonstrated over many years, in facilitating world trade of electrical and electronic products through the application of harmonised third-party certification to IEC international standards of those products and the worldwide acceptance of those certificates.
With this in mind, a decision was taken at the CAB meeting in Boston in June 2012 to investigate the development of a framework for a global energy efficiency labelling program. The mandate given to WG 12 of the CAB was to work in conjunction with expertise provided from the IEC National Committees (NCs) of countries that already have existing energy efficiency labelling programs and from the NCs of countries without such programs. Further, it was expressly stated that any concrete proposals for methods, services or labels should be developed depending on market demand and the availability of suitable international standards that could provide a common technical basis.
More information on the proposal can be found in the presentation given by Toshiyuki Kajiya, Convenor of CAB WG12, at the IEC Asia Pacific Steering Group meeting held in Singapore in December 2012. If you have any questions or comments on the proposal or would like to contribute to the development process, please contact Mr Kajiya at .
Dates for your Diary
Come On Labels project seminar on new energy labels
15 March 2013 – Brussels, Belgium
IEC TC34 working group meetings
8-11 April 2013 - Seoul, Korea
22-23 April 2013 – Jakarta, Indonesia
eceee 2013 Summer Study on energy efficiency
3-8 June 2013, Toulon/Hyères, France
7th International Conference on Energy Efficiency in Domestic Appliances and Lighting
11-13 September 2013 – Coimbra, Portugal
Special Focus: Lighting Standards and Labels in the Philippines
Continuing our series of special features on national standards and labelling programmes from around the region, in this issue we are pleased to provide highlights on some of the many initiatives the Philippines are taking on lighting. More details can be found in the Philippines section of the National Standards and Labelling pages on the lites.asia website.
Background
The Philippine Government launched the National Energy Efficiency and Conservation Program (NEECP) in August 2004. It sets the background for the implementation of energy efficiency and conservation programs through the promotion of efficient use of energy in the economy in the period 2005-14.
Department Administrative Orders (DAOs) are used as the legislative basis for regulation concerning energy efficiency in lighting products.
In 2005, the Government of the Philippines, with GEF support, initiated the Philippine Efficient Lighting Market Transformation Project (PELMATP) to move towards efficient lighting by integrating various energy efficient lighting programs and practices into standards, labelling programmes and promotional activities. Building on PELMATP achievements, the ADB-supported Philippine Energy Efficiency Project (PEEP) was initiated in 2009.
Lighting phase-out
In February 2008, the President of the Philippines called for a ban on incandescent lamps by 2010 and there is currently an initiative in the House of Representatives, particularly from the Committee on Ecology, to develop and pass a bill for the phase-out of inefficient lamps in the country. At this point it is unclear when the bill will be approved.
Test method and performance standards
The Philippine Department of Trade and Industry’s Bureau of Product Standards (BPS) is the government agency mandated to develop national standards for product safety and quality.
The development process is carried out via a technical committee approach. The Technical Committee is composed of the Bureau of Product Standards, the initiating Government agency (the Department of Energy in the case of national standards for energy efficiency and labelling), representatives from the industry (manufacturers, importers and suppliers), consumer and professional groups, research institution, testing laboratory and academe. A Technical Working Group composed of technical representatives from the same composition as the Technical Committee is normally created to facilitate the drafting of the standard.
The technical committee approach follows a formal procedure which includes research and testing, consultation, approval stages and promulgation and takes from four months up to three years to complete. The process flow chart is shown below.
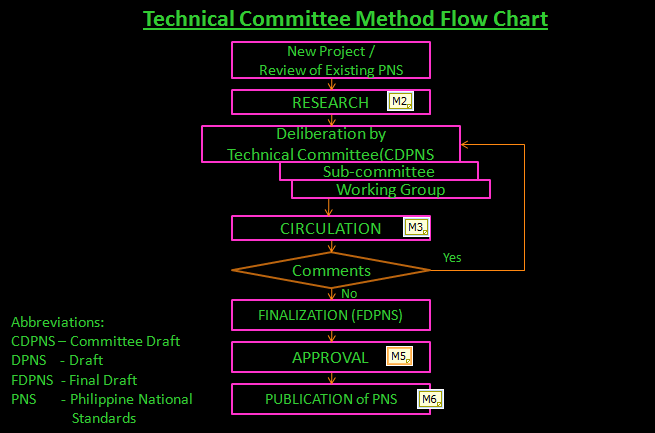
The Philippines is a full member of IEC. Its membership is represented by the Philippine National Committee of the IEC (PNC-IEC), an industry organization fully supported by the Bureau of Product Standards of the Department of Trade and Industry. This committee has a license agreement to use IEC publications, attend the IEC General Meetings, Technical Committee Meetings and take part in other related IEC Regional meetings and workshops. It is a participating member of SC34A (Lamps) and observer member of TC34 (Lamps and Related Equipment) and SC34D (Luminaire).
The Philippine national standards are aligned with IEC Standards for performance and safety, however, in the case of the standards for Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) and energy labelling requirements, the concerned Technical Committee identifies various sources for information materials.
Test Method Standards
Philippine test method standards are in place for CFLs, ballasts and linear fluorescent lamps.
Performance Standards
Philippine performance standards are in place for CFLs, linear fluorescent lamps, incandescent lamps and ballasts.
Environmental or health-based standards
Under the Philippine National Eco-labelling Program, eco label requirements are being implemented voluntarily for some lighting products, namely linear fluorescent lamps, ballasts, induction lamps and light emitting diodes (LEDs) 3W and below.
Labels
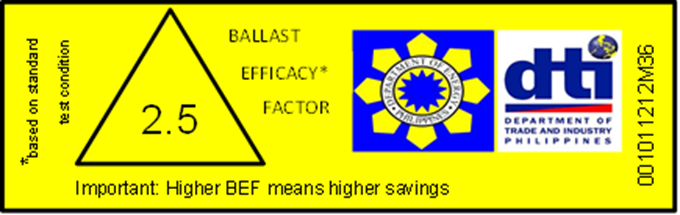
It is anticipated that with the passage of the proposed Energy Conservation Bill, the Energy Labelling Program will soon be handled solely by the Department of Energy. Mandatory labels are in place for CFLs, fluorescent lamps and ballasts.
 |
|
Enforcement of regulations
The Regional Operations Group (ROG) of the Department of Trade and Industry is tasked with enforcement activities for regulated products.
The Department of Energy and the various Regional and Provincial offices of the Department of Trade and Industry conduct joint market monitoring activities to determine compliance to the energy standards and labelling program. Enforcement is vested upon the Department of Trade and Industry.
The Philippine Product Safety and Quality Foundation (PPSQF) is non-stock/non-profit foundation that works closely with Philippine Industries and the Bureau of Product Standards in upholding and promoting safety and quality and conducts regular market surveillance activities of regulated products.
Testing capacity
Testing of lamps and related equipment is undertaken by four main institutions in the Philippines.
Energy Research and Testing Laboratory Services
Energy Research and Testing Laboratory Services is the Philippines’ national lighting test laboratory. It is an integral part of the Department of Energy's effort to explore and develop indigenous energy resources and to promote energy efficiency by providing quality and timely analytical and technical services with the best trained, motivated personnel using state-of-the-art equipment. It formulates policies, plans and programs in support of the upstream and downstream activities of the agency and promotes energy efficiency and conservation, through laboratory research, geochemical, and physical/calibration testing of lighting/lighting systems and household appliances.
Bureau of Product Standards Laboratory Testing Center (BPSTC)
BPSTC conducts safety testing for lamps and related equipment listed under mandatory certification.
Scientific Environmental and Analytical Laboratory and Services, Inc. (SEALS)
SEALS conducts safety and performance tests (except ballast) for lamps and related equipment listed under mandatory certification.
Integrated Institute of Electrical Engineers Foundation
IIEEF conducts safety (for linear and CFLs) and performance tests for lamps and related equipment including ballasts listed under mandatory certification
Sustainability/End-of-life treatment initiatives
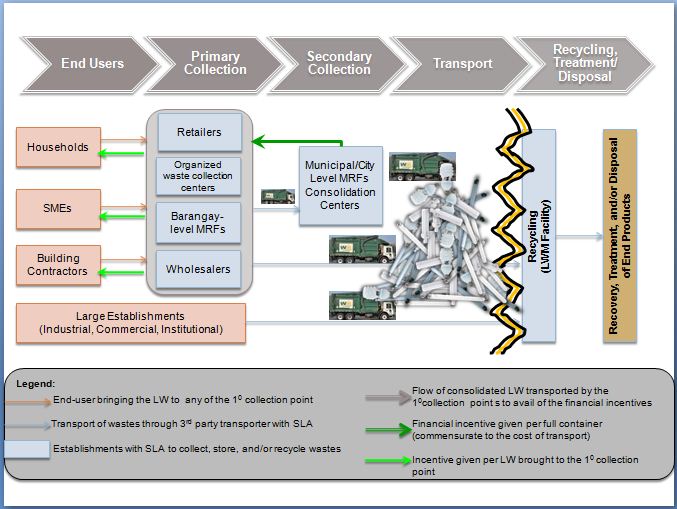
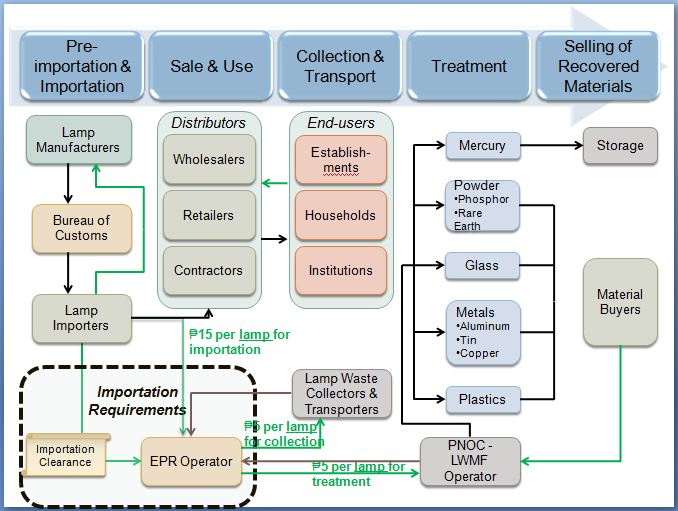
In 2012, implementation of an EPR (Extended Producers Responsibility) system and pilot lamp waste management (LWM) facility commenced in the Philippines. The facility has a capacity of six million lamps per year and funding for its operation will be provided through the EPR system. The system includes collection, transport and recycling/recovery of mercury and is illustrated diagrammatically in the following figures. This initiative is intended to create a viable business model for lamp waste management for replication throughout the country.
Philippines lighting products EPR model
Philippines LWM model